In making variety of shapes and surfaces, the right and accurate cutting tool must be selected. There are many types of cutting tools for router machine. Every types of cutting tools have their own function and capability. It depends on types of material and shapes that need to be produced.
(a) Features of cutter
Two processes are needed for routing operations. First one is cutting away large amounts of material by leaving a poor surface finish, we called it roughing cutting and another type of process is finishing by removing a smaller amount of material and leaving workpiece in a good surface finish. These two types of process is depends on teeth of cutter used, for roughing cutter may have serrated teeth for breaking the chips of workpiece into smaller pieces, and for finishing process may have many of tooth for cutting away material smoothly. However, the large number of tooth leaves little place for chips removal, so they are less appropriate for removing large amounts of material.
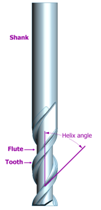
The shank is the cylindrical (non-fluted) part of the tool which is used to hold and locate it in the tool holder. A shank may be perfectly round, and held by friction, or it may have a Weldon Flat, where a set screw, also known as a grub screw, makes contact for increased torque without the tool slipping. The diameter may be different from the diameter of the cutting part of the tool, so that it can be held by a standard tool holder.
Flutes and tooth is the part other than shank part. The flutes of the router bit are the deep helical grooves running up the cutter, while the sharp blade along the edge of the flute is known as the tooth. The tooth cuts the material, and chips of this material are pulled up the flute by the rotation of the cutter. There is almost always one tooth per flute, but some cutters have two teeth per flute. Routing cutters may have from one to many teeth (2, 3 and 4 teeth being the most common). Typically, the more teeth a cutter has, the more rapidly it can remove material. So, a 4-tooth cutter can remove material at twice the rate of a 2-tooth cutter.
Flutes should be designed with the appropriate angle to allow the tooth to enter the material gradually and reduce vibration. If the flutes were designed without angle can cause vibration, less accuracy and low surface quality because the whole tooth would impact the material at once. Typically, finishing cutters have a higher rake angle (tighter helix) to give a better finish.
(b) Type of cutting tool

1. Face Mill
A face mill is designed for facing instead of making a pocket. The cutting edges are located along its sides and cut in horizontal direction. Multiple teeth distribute the chip load, and the teeth are normally disposable carbide inserts. This combination increase the efficiency of face milling.

2. End Mill
End mill is a cutting tool that has teeth at the end, as well as on the sides. They are usually made from high speed steel /cemented carbide, and have one or more flutes. They are commonly apply in a vertical mill operation such as slotting, pocketing, shaping and so on.

3. Fly Cutter
Fly cutter is used for face milling and their individual cutter are replaceable. It is usually a standard left-hand turning tool that held at an angle of 30 to 60 degrees. Fly cutters with two tool bits are often take the form of a bar of steel with tool bit fastened on each end. Often these bits will be mounted at right angles to the bar’s main axis.

4. Ball Nose
Ball nose cutter is used to slot drills, but the end of the cutter is hemispherical shape. It is ideal for machining 3D contoured shapes in machining center. They can also be applied to add a radius between perpendicular faces to reduce stress concentrations.

5. Conical
Conical cutter is used to cut conical shapes on material surface. These tools are stocked in angles ranging from 10° – 120°. Usually this cutter is used for sculpture, sign making and calligraphy word.
